What is a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
What is a vaginal yeast infection?
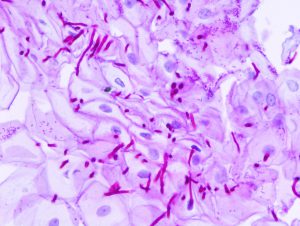
One of the most common infections in women is a vaginal yeast infection. The infection is caused by the organism called Candida, which is actually a fungus. Also referred to as vaginal candidiasis, this yeast infection can present with watery vaginal discharge, irritation and intense itching of the vulva and vagina.
Many women don’t know what is a vaginal yeast infection and often confuse it with bacterial vaginosis or an STD. That’s why it’s really important to know what are the symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection.
The vaginal area appears reddish and the discharge either has no smell or a smell resembling yeast. Vaginal yeast infection affects nearly 70-80% of women at some point in their life. On average, most women experience a minimum of two episodes in their life.
The important thing to note is that vaginal candidiasis is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection, but it can be spread to the partner after oral sex (mouth to genital contact).
Today, there are effective medications to treat vaginal candidiasis. For those women who have recurrent Candida infections (at least four more within a 12 month period) long-term treatment is necessary and some may even require being on maintenance treatment for a long time.
What are the symptoms of vaginal yeast infection?
The symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection can vary from mild to severe and include the following:
- Irritation and itching around the vagina and vulva
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Discomfort or a burning sensation during sexual intercourse
- Mild swelling and redness around the vulva
- Mild pain around the vagina
- Red rash
- Watery vaginal discharge
- There may also be a vaginal discharge that appears cheesy in nature and has no odor.
What is a complicated vaginal yeast infection?
There are some women who develop a complicated vaginal infection. This may include developing:

- Severe symptoms such as swelling, unrelenting itch and excessive redness.
- Cracks, sores and tears of the vaginal lining.
- At least four or more Candida infections in 12 months.
- A yeast infection that is not due to the usual Candida albicans but some other strain.
- A yeast infection during pregnancy.
- A yeast infection during uncontrolled diabetes.
- A weak immune system because of use of certain prescription medications or having HIV.
Why does one develop a vaginal yeast infection?
The vaginal infection is caused by a fungus called Candida. This fungus is normally present in the vaginal area, along with bacteria known as lactobacillus. In normal circumstances, the lactobacillus bacteria generates an acidic environment that limits and controls the growth of Candida.
If this delicate balance is disrupted for whatever reason, the Candida starts to thrive and the end result is a Candida infection. When Candida starts to multiply it tends to cause burning pain, watery discharge, itching and a cheese-like discharge.
What are risk factors for a vaginal yeast infection?
According to WebMD, some of the risk factors that can lead to an infection include:
- Becoming pregnant
- Having uncontrolled diabetes
- Use of antibiotics that can diminish the levels of lactobacillus bacteria and alter the pH of the vagina.
- Depressed immune system or taking a medication like a corticosteroid
- Use of oral contraceptives – especially those with high levels of estrogen
- Being Overweight
- After sexual activity especially oral-genital contact. However, it is important to remember that Candida is not considered to be a sexually transmitted infection. Even women who do not have oral sex can acquire this infection.

In the majority of women, the yeast infection is due to Candida albicans. However, in some cases, other strains of Candida, such as Candida glabrata or Candida tropicalis, may also cause the vaginal infection. These infections tend to be more difficult to treat and usually require combination treatments.
How is a diagnosis of vaginal yeast infection made?
Once you have symptoms, the healthcare provider will ask you about the presenting features and perform a pelvic exam. In most cases, the diagnosis of a yeast infection can be made from the history and clinical exam. However, in some cases, the vaginal secretions will be tested for the fungus.

How is vaginal yeast infection treated?
The treatment of a vaginal yeast infection depends on whether this is a simple or complicated infection.
Simple yeast infections
For women who have a simple uncomplicated vaginal yeast infection, the treatment is as follows:
Short course treatment: there are several antifungal medications available as ointments, creams, suppositories and tablets. The majority of these antifungal regimens may require one, three or seven days to clear the Candida infection. The antifungal medications for yeast infection available over the counter include the following:
– Gyne Lotrimin
– Monistat (miconazole)
– Gynezol
– Femstat
– Vagistat-1
Prescription yeast medications include:
– Lotrimin
– Micatin
– Terazol
– Diflucan
These prescription medications are more concentrated and thus only need to be taken for a short period.
Important Facts about Antifungal Medications
- The vaginal creams are to be used at bedtime and can be messy to use. If you use them during the daytime, they can leak out. These creams work fast and can rapidly relieve the itching and redness.
- When using vaginal creams one must abstain from sexual activity if you use a diaphragm or condom for birth control. The oil in the cream can damage the condom and diaphragm. You may need to use some other form of birth control instead.
- The tablets and suppositories are easy to use, less messy than the creams and less likely to leak out. Further, the tablets and suppositories tend to work faster and only a few dosages are required.
- Side effects of the creams include irritation or burning during initial application. However, these adverse effects are mild and usually disappear spontaneously.
The type of treatment will depend on your symptoms and what you prefer. Some healthcare workers prescribe a single oral dose of Diflucan and others recommend vaginal creams and suppositories.
If you are pregnant, you should not use any pill but instead, adhere to the vaginal suppositories and creams. The treatment will usually last 3-7 days.
Complicated yeast infection
There are some women who have a complicated vaginal yeast infection and in such cases, more aggressive treatment is required. The treatment will usually include:
- A longer course of vaginal treatment with the same medications used to treat the simple infections. The course of therapy may last 7-14 days. One may use a cream, tablet, ointment or a suppository.

- If the infection is severe, then you may be prescribed several doses or the oral pill (Diflucan). The oral pill is not recommended for pregnant women who are instead treated with creams or vaginal suppositories.
- For women who have recurrent Candida infections, you may be placed on a maintenance treatment to prevent future infections. Once the initial infection is clear which may take 7-20 days, then you will be prescribed an oral drug (e.g. Diflucan) for 3-6 months. Some healthcare providers also prescribe a vaginal suppository that is used once every 7 days instead of the pill.
- Unless your partner has symptoms, there is no treatment required. However, during the active infection, it is important to abstain from vaginal oral sex.
Are there are alternative treatments for vaginal yeast infection?
Over the years, many alternative treatments have been promoted for treatment of vaginal yeast infections. Many of them are supported with substantial clinical studies, while others still lack scientific evidence for their effectiveness.
Some of the common alternative therapies supported by scientific research include:
- Boric acid is available as a vaginal suppository and is often used to treat chronic cases or those infections not caused by Candida albicans. The boric acid suppository is only used twice daily for 14 days. However, this agent can induce moderate skin irritation. It should also be kept out of reach from children, as ingestion can be fatal.
- There are many reports that yogurt and probiotics may relieve symptoms of a vaginal yeast infection. Probiotics can help women rebuild healthy levels of friendly bacteria to inhibit Candida overgrowth, speed up recovery from a yeast infection and avoid future infections.
Not only are probiotic supplements cheaper than most medications, but also have almost no side effects. Plus, probiotics also have many other health benefits like boosting the immune system, detoxifying the digestive tract and reducing the risk of urinary tract infections.
- One of the probiotic supplements that contain well studied probiotic strains for vaginal yeast infection is Renew Life Ultimate Flora Women’s Complete. In fact, now there are even tampons available that are fortified with probiotics. The Saforelle Probiotic Tampons have been shown to enhance the growth of lactobacilli in the vagina and reduce symptoms of Candida.
- There are many other natural remedies supported by scientific evidence, click on each to learn more: Aloe Vera, Ginger, Olive Leaf, Coconut Oil, Honey.
How can I prevent vaginal yeast infections?

In order to decrease the risk of vaginal yeast infections, you can do the following:
- Avoid wearing tight constrictive pantyhose or undergarments.
- Wear undergarments made of cotton.
- Dress in skirts or loose-fitting trousers.
- If your clothes do get wet, change them often- especially your workout attire and bathing suits.
- Limit the time you spend in saunas, hot showers and hot tubs.
- Avoid using antibiotics without a reason. In most cases, the common cold is best treated with rest, fluids and the occasional Tylenol.
Read my article to learn more about preventing vaginal yeast infections.
Conclusion
Vaginal yeast infections are quite common in women of all ages. This infection can affect the quality of life because of its symptoms.
While there are effective treatments available, most experts recommend that it is better to prevent the infection in the first place. One of the best ways to prevent vaginal yeast infection is regular consumption of probiotics.
To learn more about vaginal yeast infections, check the video below:
If you’ve got any questions or comments please share in the comment section below.


I have to admit, I’d already had a number of yeast infections before I even knew what they really were… each and every time, they managed to clear up on their own within a few days-a week. Would you say it’s better to allow them to clear of their own accord (as long as it’s not causing TOO much irritation), or to use alternative treatments?
Thank you for sharing!